AGI: What is it, and what to expect from it?

AGI is an acronym for Artificial General Intelligence, which stands for strong artificial intelligence. This type of AI blurs the line between human and machine intelligence and is the main topic of this article.
General artificial intelligence is defined as the intelligence of machines that allows them to understand, learn, and perform intelligent tasks in the same way that humans do. Although AGI does not officially exist in practice yet, comprehensive research and development are underway, which suggests that, theoretically, AGI can perform new tasks that it has never learned and other creative actions that only humans were previously capable of.
AGI is AI, but it is an updated and much more powerful version. Let’s take a closer look.
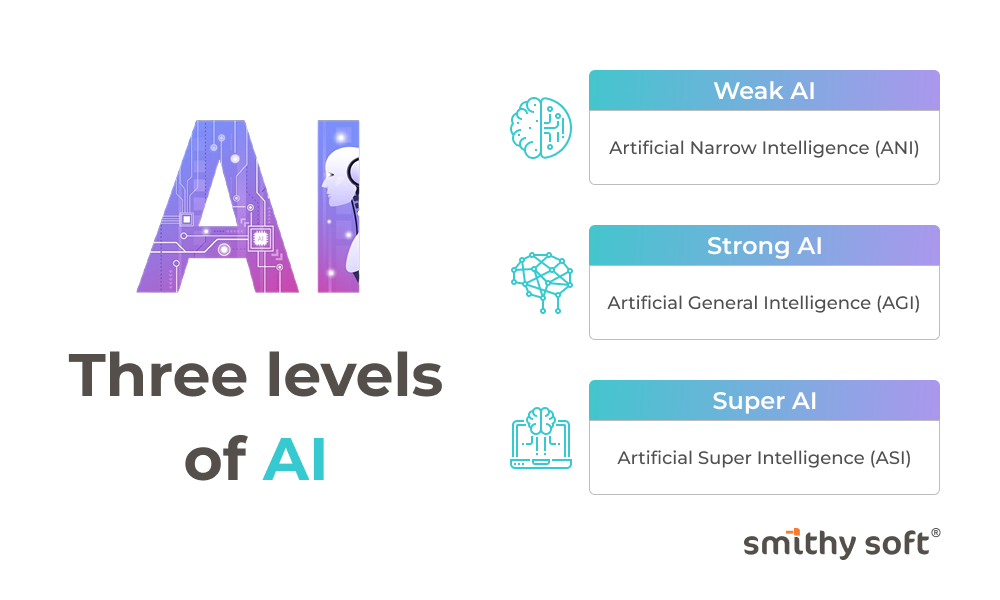
Three levels of AI
General artificial intelligence is considered one of the three main types of artificial intelligence.
- Weak AI: Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
- Strong AI: Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
- Super AI: Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) or Weak AI, also known as AI, is the vast computer science field that works on pre-programmed rules, algorithms, and supervised learning to perform tasks in adherence to specific instructions within a certain context.
Weak AI examples include chatbots, spam email filters, smart assistants such as Siri and Alexa, unmanned cars, GPS and navigation apps, autocorrection features, and recommendation mechanisms on Netflix, Amazon, etc.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is a subset of AI designed to emulate human cognitive abilities by leveraging unsupervised learning to solve problems on its own and adapt to a range of contexts.
Strong AI examples: generative AI, robotics, and advanced chatbots, as well as robotic machines that for now exist only in Scy-fy
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) refers to an artificial intelligence of a hypothetical kind that might be invented in the future that surpasses the intelligence and cognitive abilities of humans in areas such as creativity, planning, social problems, and general understanding. ASI would not only mimic human behavior but would also be able to learn, adapt, and evolve on its own without human intervention, raising questions about its impact on the future of humanity and the ethical aspects of its use. Superintelligence will be fully self-aware and will surpass human intelligence. It could do a lot more and perform for a much longer time than humans do. Currently, superintelligence is hypothetical.
What features are distinct for AGI?
In this regard, many scientific and technological discussions are currently underway, which generally boil down to what determines a person’s intelligence, level of mental activity, and self-awareness and how to “transfer” all this to machine standards.
Intelligence is a concept that is difficult to define or give a quantifiable assessment. For more than a century, cognitive scientists have been trying to identify the fundamental components of human intelligence. IQ tests and other scores used to quantify general intelligence are only snapshots of current cultural values and environmental conditions. The term “general intelligence” is even more vague and complex, and it is not yet known exactly how it can be measured in machines.
At the same time, AI experts distinguish the following features of Strong AI:
- Meaningful learning. Rather than learning from massive datasets as current AI models, AGI will have the ability to autonomously analyze and understand information in a way that more closely resembles human thinking. AGI is an untrained and unprogrammed tech that can respond to complex queries, similar to recent LLMs such as GPT-4 and Google's Gemini.
- Knowledge transfer and summarizing. The AGI system should be able to use the knowledge gained in one area to solve problems in another without having to relearn.
- Independent problem solving. AGI will not only process the data but also be able to ask questions, formulate hypotheses, independently test different solutions, and make choices.
- Situational awareness and adaptation. AGI systems must understand the context in which they operate and dynamically adapt their actions to changing conditions.
- Human behavior imitation. Features like flexibility, the ability to calculate options, and make choices considering countless scenarios.
AGI Technology Basics
The efforts to create AGI systems are presently underway – they are being explored and stimulated by new developments. Some of them passed successful tests and have good prospects. Examples include:
- Neural networks are considered to be the backbone of modern AGI research. They are modeled on the architecture and functions of the human brain. Trained on huge datasets, these networks consist of interconnected nodes that resemble neurons and synapses. Neural networks can be defined as super-intelligent learning algorithms that change the way machines process information and make decisions.
- Deep learning is a type of AI that teaches neural networks to understand and find patterns in large amounts of data. Experts use deep learning to create systems that can understand text, audio, images, video, and other types of data. For example, developers use Amazon SageMaker to build simple deep-learning models for the Internet of Things (IoT) and mobile devices.
- Generative AI is a type of deep learning that can create unique and realistic content using what it has learned. Generative AI models are trained with enormous sets of data, which helps them respond to people’s questions with text, audio, or visuals that look and feel like human-made things. Some examples of generative AI algorithms that organizations use to solve complex tasks are LLMs from AI21 Labs, Anthropic, Cohere, and Meta.
- Machine Learning Approaches comprise a range of methods that enable machines to learn without the need for explicit programming. In machine learning, the following specific techniques are used:
- Supervised Learning (each labeled data point has a corresponding desired output, and the machine is trained using this data. By learning to connect the input data to the intended output, the machine can predict new, unknown data).
- Unsupervised Learning (the machine is trained on unlabeled data, and it is up to the machine to find patterns and connections within the data. This is very helpful for dimensionality reduction and anomaly detection activities).
- Reinforcement Learning (it involves placing the AI through trial and error to learn using a simulated environment. AI can learn the best way to achieve its goals by rewarding desired behavior and punishing errant behavior.)
- NLP: Natural language processing is a branch of AI that allows computer systems to understand and generate human language. NLP systems use computational linguistics and machine learning technologies to turn language data into simple representations called tokens and understand their contextual relationship.
- Computer vision enables spatial information to be gained from visual data and its analysis. Self-driving cars use computer vision models to analyze real-time feeds from cameras and navigate the vehicle safely away from obstacles. Deep learning technologies allow computer vision systems to automate large-scale object recognition, classification, monitoring, and other image-processing tasks.
- Adaptive Robotics: robots are learning to perform tasks without explicit programming. For instance, some robots can navigate complex environments, learn from mistakes, and adapt to new challenges, which are all essential elements for AGI development.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces: innovations in this area seek to link the human brain directly to computers, thus enabling seamless interaction between users and AGI systems. This could transform the way humans work, communicate, and access information.
Prospects for using AGI
As wide as one can imagine! AGI is designed to do everything a human can, bringing some advantages to the table. For instance, it speeds up processes and removes the monotony of work - the concepts that often result in a drop in productivity in humans.
AGI will be able to perform a job for long hours without interruption with the same performance level. This will allow you to perform tasks with utmost concentration, no distractions, and without getting tired.
AGI will be able to perform dangerous jobs, like mining, working with chemicals, biological materials, etc.
AGI can optimize business processes considerably, starting with task automatization and finishing with strategic planning.
It will predict and calculate the risks and quickly approve the most effective decisions in emergencies. For example, to foresee a catastrophe, to outline optimal evacuation routes, to call the necessary rescue services, etc.
AGI tutors can tailor teaching methods to each student’s learning style, pace, and interests. They can leverage XR tools to design an engaging and more effective learning experience. Students’ assessment will not depend on the teachers’ mood and individual attitude towards each particular student.
In healthcare, AGIs have the potential to help out with complex diagnosis formulation and create customized treatment plans based on many factors.
AGI would have also helped companies to analyze market trends and provide operational data required for strategic decisions.
In public policy, AGI is capable of modeling the consequences of different policy options.
Risks of General Artificial Intelligence
Ethical questions: There is reason to doubt whether AI can understand human ethics, so humans may have to confront AI that does not adhere to human ethical standards.
Social inequality: AGI needs capital and resources that only large corporations have, concentrating even more power in the hands of a few companies.
Lack of legal safeguards: Laws still lag behind weak artificial intelligence, so AGI is likely to have no legal restrictions and could potentially be used for malicious purposes.
Unemployment increase: Developing artificial intelligence that can mimic and surpass human abilities could raise well-founded fears of job loss due to automation.
False solutions: In weak artificial intelligence, problems have already arisen where embedded systems were created with biased data. This can lead to AI making erroneous or, at worst, discriminatory decisions.
Cybersecurity: who and how will influence and control AGIs? And how can we make sure that it is used for the benefit of all? Wouldn’t a smart cyber monster be created all of a sudden that would assume that humans are harmful and endanger its existence?..
CONCLUSIONS
In a sense, superhuman artificial intelligence is already present among us quite massively, but so far in the form of weak AI. It benefits us, we use its full capabilities and still do not fully understand its limits.
As long as we control this process, we can influence it. Therefore, people are the main responsible creators and perpetrators of certain decisions and events in this world.
As soon as there is something, some kind of superintelligence that surpasses man, we will cease to be the highest step of the evolutionary development of this planet.
Therefore, it is worth treating artificial intelligence as a certain tool FOR a person, and not instead of. Then, the risk of using this tool will be as great as people want it to be. After all, any tool can be used both for good and for harm. The main thing is that it will be decided by people, and not by someone (or something) instead of us.


