Anatomy of a URL You Should Know

URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator and is a standard for specifying the address of a resource on the Internet. It is used to identify and locate resources such as web pages, images, videos, audio files, documents, and more on the World Wide Web.
A URL not only points to the location of a resource (page, video, file, etc.) on the Internet but also provides information about the request, page number, or even the website architecture.
At first, it may seem like you don’t need to know the different parts of a URL if it contains your company name. However, website URLs can play a significant role in elevating your site's efficiency and search engine optimization (SEO) strategy.
So, let's break down the various parts of a URL and understand how different URL structures can impact your overall marketing strategy.
Essential Parts of a URL
A simple URL consists of at least three parts.

A complex URL can contain up to nine parts.
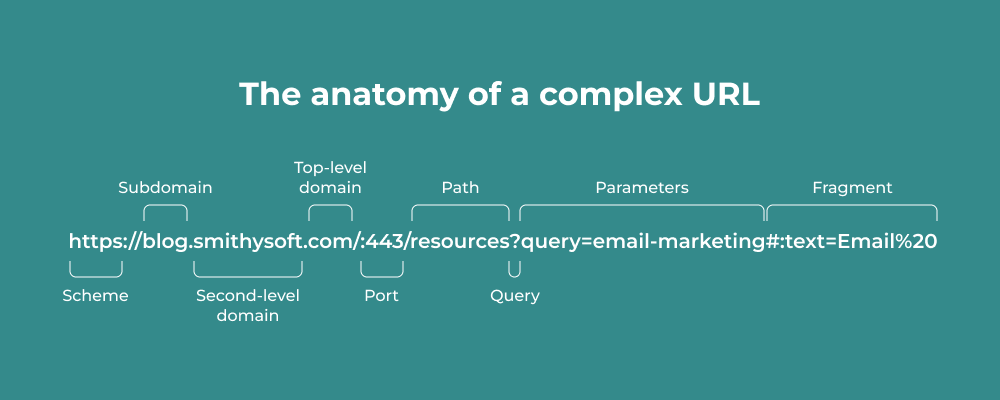
Let’s take a closer look at these parts.
1.Protocol or Scheme
The first part of a URL is a Protocol. It is a set of rules for how files are displayed, formatted, or transferred over the Internet.
The “http” stands for the Hypertext Transfer Protocol and indicates that the page should be displayed in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). Other protocols include File Transfer Protocol (FTP) for file transfer and Mailto, used by mail servers to send emails.
By the way, https is the secure version of http. It stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. Nowadays, HTTPS is the most common scheme. It tells your web browser to encrypt any information you enter onto the page, like your passwords or credit card information, so cybercriminals can’t access it. This security protocol protects your website visitors thus implementing it will help your site rank better on Google.
Users don’t need to enter the protocol when typing your website’s URL into their web browser. These symbols will be added automatically.
2.Domain Name
That is the name of a website or another resource you want to visit. For example: https://smithysoft.com
Domain names must be unique as they define the address of a website. They’re one of the most important parts of a URL because even if you don’t know the full URL of a website, you can quickly search on Google using the company’s name to find its website.
A domain name comprises two smaller parts: the name of the corresponding website (Second-level domain) and the top-level domain (TLD). The top-level domain is also known as the domain extension. In https://smithysoft.com, the top-level domain is .com.
Top-level domains represent the type of your organization. For example, government websites use the top-level domain .gov, while commercial companies typically use .com. Other top-level domains are .edu, .net, .org, and many others. Some websites also use a “country code top-level domain” or ccTLD to target their local audience. These include .uk for the United Kingdom, .de for Germany, and .in for India.
When setting up a new website, it's worth spending some time carefully considering the domain name you will use. It should be unique and attention-grabbing but at the same time clear and easy to remember.
Your choice of TLD also matters; “.com” is the most popular option among users but you can choose a top-level domain that better suits your niche or industry.
3.Subdomain
It determines what specific content of the website should be displayed. Subdomains vary depending on the type of pages and topics. For example, a website with a blog might use “blog” as a subdomain: https://blog.smithysoft.com/
The most common subdomain is “www,” which is a general symbol for any resource on the Internet. The “www” subdomain indicates that the website uses HTTP or HTTPS. However, this subdomain is no longer necessary when entering a URL on the Internet.
Subdomains provide a hierarchy to your website content, allowing you to classify different areas of your website.
4.Subdirectory
The subdirectory is located after the TLD in the URL. Also known as a nested folder, it helps users understand their location on a website.
For example, the URL of this article: https://blog.smithysoft.com/author/smithysoft/ Here, the subdirectory is “author.” By the name of this subdirectory, you can determine that in the blog, you are reading the “author” section – smithysoft.
Of course, the name of your subdirectory can be anything that helps organize your content and assists people and search engines in understanding different types of content on your website.
5.Port
URLs can also include ports. They stand for specific server ports to which the browser is connected. Ports are indicated by numbers. The port number must be a 16-bit unsigned integer: in other words, a whole number from 0 to 65535, inclusive.
For an HTTP URL, the default port is 80, and 443 for HTTPS. The URL does not require specifying a port number if the port used is the default one.
It’s important to note that port numbers are not IP addresses. Instead of identifying a particular machine in a network, ports identify applications on a system.
6.Path
If your end goal is to visit the main page of a website, all you need is the protocol and the domain name: https://smithysoft.com. However, each page or file on a website also has its URL. For example: https://www.smithysoft.com/our-cases.
The part after the TLD is known as the “path” because it directs the browser to a specific page on the website—in this case, the page with our cases.
Ideally, the path should be easy to understand for both humans and search engines. If correctly chosen, it will help your posts achieve higher rankings on search engine results pages. It means you should avoid URLs like this: https://example.com/index.php?p=4556
7.Query
If your website has a search bar, users will see the query they are searching for in the URL. Whenever there is a question mark in the URL, it informs web browsers and users that a query is being executed.
The beginning of the query starts after the question mark in the URL. For example: https://www.google.com/search?q=smithysoft, where the query is “smithysoft.”
The query string defines the data parameters requested from the website's database.
Next, we’ll look at the parameters.
8.Parameters
Parameters are the values queried during a search. The parameter can be a number, encrypted value, search term, or other data found on the website. URL parameters contain a key and value, separated by an equal sign (=). A URL can enclose multiple parameters, each separated by an ampersand (&).
For example https://www.google.com/search?q=smithysoft&oq=smithysoft&gs…
URL parameters provide users and search engines with additional information about a page to filter and organize the website's content. They can also serve as page identifiers in an archive or during site searches.
Another standard use of parameters is tracking specific marketing campaigns in analytics tools like Google Analytics.
9.Fragment or Anchor
Fragments are an optional component of a URL, typically placed at the end with a hash (#). They are not sent to the server with the request but are used by the browser to move the user to a specific page section.
The primary function of an anchor is to provide direct access to a specific place on the page, which is convenient for navigation, especially on extensive or lengthy web pages.
For example, in this URL, the anchor is specified as “#section1”: https://www.example.com/path/to/resource#section1
In this case, if a user follows a link with this URL, the browser will automatically scroll the page to the section or element of the page with the identifier “section1”. The use of anchors is particularly common in web documentation, blogs, and many single-page websites where sections display different parts of the content.
SOME IMPORTANT TIPS
- Use the HTTPS protocol. As mentioned earlier, HTTPS is the most common protocol used in URLs. It is because it encrypts personal information, making it more difficult for criminals to discover it. By using this protocol on your pages, you help protect your visitors.
- Keep URLs simple, short, and relevant. Overly complex URLs can be challenging for users and search engines to read. Keeping URLs short, simple, and relevant to the content helps avoid confusion and make your pages easily accessible.
- URLs are one of the main reasons you might be getting penalized by search engine algorithms. When you are penalized for incorrect URL structures or other SEO errors, it damages your website’s authority and rankings on search engines.
- Changing the domain name is possible, but it’s best to do it as a last resort. Even if done carefully, changing your website’s domain name will impact your ranking in the search engine for some time as Google and other search engines will need to adapt to the changes. It will also affect your search traffic.
- Regarding the subdomains or subdirectories, you can create as many subdomains as you like or not use them at all. The difference is that Google considers subdomains as separate websites. Subdirectories though are seen as a part of one website. It means that the search engines will rank your subdomains separately, while your SEO ranking will be distributed among your domain and subdirectories. For bloggers, startups, or small businesses with limited time and resources, using subdirectories can help rank faster than a subdomain.
- As for URL shortening, it's a technique to significantly reduce the length of a URL while still directing it to the intended page. It is convenient for social media and looks aesthetically pleasing. There are several URL shortening services, both paid and free. However, some service providers, including search engines, have started to shy away from URL shortening programs as they often become targets for abuse by spammers who hide malicious software inside shortened URLs.
In summary, the URL plays a crucial role not only in the usability of your site but also in search engine results, impacting your effectiveness and interaction with potential users.


