ANGULAR vs VUE

Framework Backgrounds
- Angular is a framework developed by Google; Google also uses Angular so it is unlikely that Angular will disappear one day. It will be maintained and continuously improved.
- Vue is a “standalone” project that is not built by any company. It used to be a one-man project of Evan You. Nowadays, it has a dedicated team of core contributors that work for Vue.
Philosophies
- Angular definitely is the “biggest” framework of the three. It’s sometimes even called a “platform” rather than a framework.
Why?
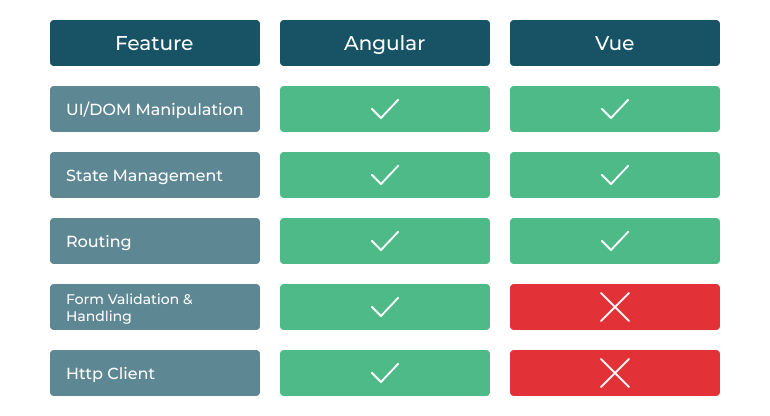
- Because Angular out of the box includes support for a lot of things. It helps you with controlling the UI, reacting to user input, validating user input in forms, routing, state management, sending Ajax Http requests, providing offline support & PWA capabilities, testing, building your application, managing multiple applications, and connecting them and much, much more!
- Vue is a framework that is a lot like Angular. It’s not as “big” as Angular, but it definitely includes more features than React does. Vue does give you built-in state management, and it also has routing management. Vue includes the form validation or Http client functionalities.
Syntax
- Angular projects use TypeScript, which is a superset to JavaScript. TypeScript doesn’t run in the browser, but Angular projects include tools that will compile the TypeScript code down to browser-compatible JavaScript code under the hood.
- Vue uses regular JavaScript (though, optionally, you can also use TypeScript), and it typically uses something which is called Single File Components. It is a framework all about components after all, but like Angular, it splits template HTML&CSS and JavaScript logic apart.
Performance
There also are different kinds of performance:
- Startup performance: How fast does your web app load and become usable by the user?
- Runtime performance: How fast is your app running (i.e., how well does it re-render, update the UI, react to user input, etc.)?
Startup performance is primarily influenced by the size of the created code bundle – i.e., your own code + the framework code combined.
Runtime performance is primarily influenced by the internals of the chosen framework and how it approaches DOM manipulation and updating.
Angular apps can be a bit bigger than Vue apps – especially when we’re talking about smaller applications. In most projects, this shouldn’t really matter; it’s also just a “snapshot” since the Angular team (as well as the other teams) are constantly working on improving both startup and runtime performances.
Top Angular Apps
1. Gmail
2. Forbes
3. PayPal
Top Vue Apps
1. Nintendo
2. Gitlab
3. Font Awesome
Summary
As you can see, all frameworks have their advantages and disadvantages. The choice of the right tool for your project is unique in all cases and highly depends on the particular solution requirements.
We summarized the pros and cons of each framework so that you can get a general idea:
|
Angular |
VUE |
|
|
Size |
143k |
23k |
|
Performance |
medium |
high |
|
Scalability |
high |
low |
|
Learning curve |
hard |
easy |
|
Developers’ availability |
high |
low |
|
Developers community |
large |
small |
|
Acceptance and trust |
high |
cautious |
I choose Angular when:
- I develop a very large and complex project
- I need easy and reliable scalability
- I have Angular developers on my team
- My team can afford some time for learning TypeScript before the project starts
I choose Vue.js when:
- The project scope is on the small side
- I need high performance
- My team have no skilled front-end developers but have team members with JavaScript knowledge
- Me team do not have much time to learn a new technology



